Special registers
As well as the general purpose registers that store instructions and data as the program executes the CPU also contains some special registers that have specific purposes.
| Special register |
What it does |
| Program counter (PC) |
Stores the address of the next instruction to be executed. |
| Memory address register (MAR) |
Temporarily holds the address of the next instruction or piece of data to be fetched. |
| Memory data register |
Temporarily holds the actual instruction or piece of data that has just been fetched. |
| Accumulator |
The accumulaor stores the result |
What happens at the fetch stage?
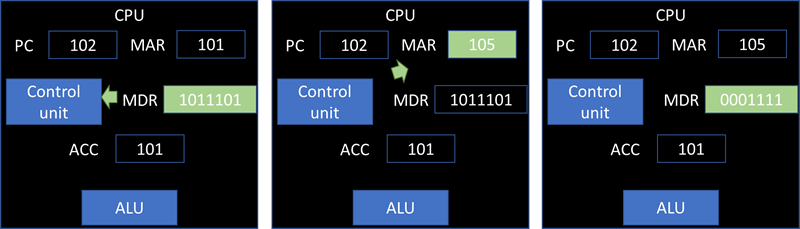
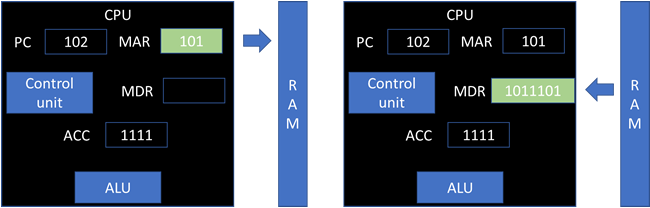
The program counter holds the address of the next instruction. This address is transferred to the memory address register(MAR). The program counter is incremented so it points to the next instruction to be executed.
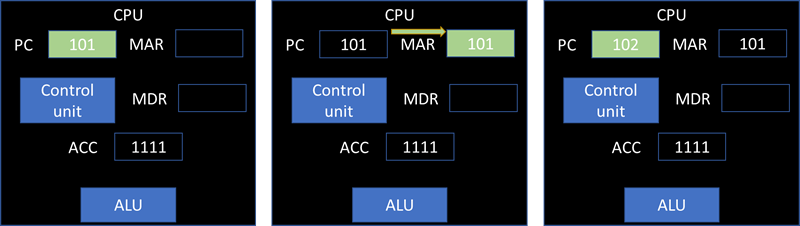
The instruction at the address specified by the MAR is returned and placed in the memory data register(MDR).
What happens at the decode stage?
The control unit decodes the instruction to work out what needs to be done. If the instruction requires some data to be fetched e.g. ADD 105, the address of the data will be passed to the MAR. If extra data is required, it
is fetched from the address in MAR and returned to the MDR.