The client server model
This is the model where a client sends a request message to server, and the server responds to the request by replying with a response message to client.
This could be a client with a web browser requesting a web page from a web server and the web server responding with the requested html files. It might be a client requesting
to store or retrieve files to or from a file server and the file server responding by storing the file in the requested location or returning the requested file.
Websocket protocol
The Websocket specification defines an API(Application Programming Interface) establishing a full-duplex 'socket' connection between a web browser and a server over TCP. This
means that there is a persistent connection between client and server, allowing both parties to send data at any time.
This makes websockets useful for a variety of purposes like online gaming, live chatrooms, location tracking
Web CRUD and REST
CRUD is an acronym for the operations that can be performed on a database:
- Create
- Retrieve
- Update
- Delete
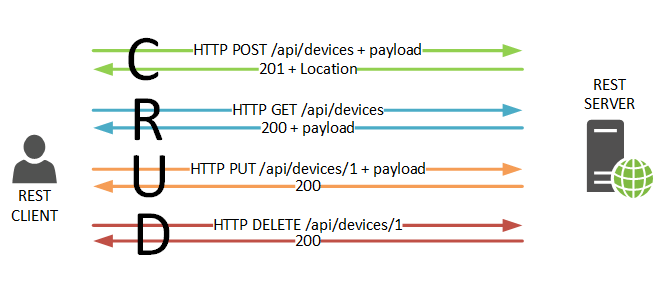
REST, short for representational state transfer, enables HTTP requests from a web CRUD application to be called using the browsers Javascript and mapped to SQL database functions
as follows:
- GET → SELECT
- POST → INSERT
- DELETE → DELETE
- PUT → UPDATE
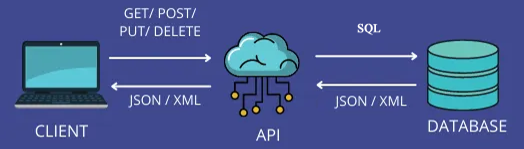
A database is connected to a web browser using REST. REST allows JavaScript to talk to the server through the HTTP commands GET, POST, DELETE and PUT. A REST API is
created and run on the server that translates HTTP requests into SQL commands. Browser JavaScript calls the API whenever it is needed. The database returns a response
in the form of XML or JSON.
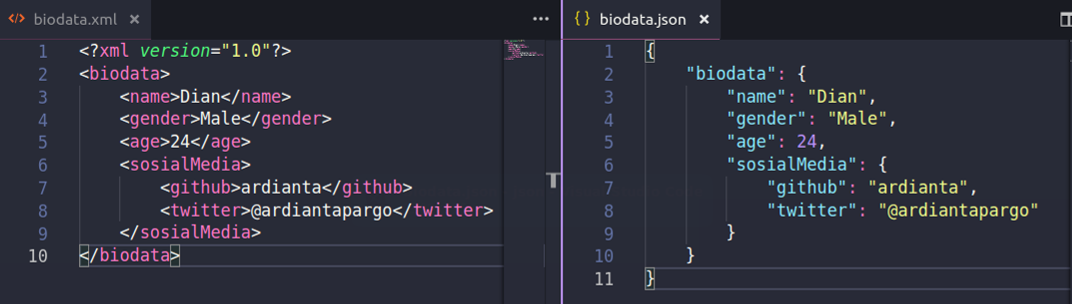
JSON and XML
JSON and XML are alternative methods that can be used to transmit data. XML uses tags like those seen in HTML with tags nested insode other tags. JSON is more like a dictionary
of key value pairs where a value can itself be another dictionary. JSON is generally preferred over XML because it is easier to read for a human, more compact, easier to create
and easier and therefore quicker for computers to parse.
Thin client vs thick client networks
The thickness of a client refers to the amount of processing and storage local to the client. Where all processing and storage is performed by the server we can have thin
clients with minimal processing ability and no storage.