Individual and market supply
Individual supply is the amount of a product one individual or firm might be willing to supply at each price in a given time period. As it is just the choice of one person or firm it can be quite volatile.
Market supply is the total supply for a product from all potential producers in the market.
The amount of grain one farmer will sell at each price in a given time is individual supply. The amount that all the grain farmers will sell at each price in a given time period is market supply.
The importance of elasticity of supply
The importance to consumers
Consumers are affected by PES in a number of ways. In some cases, there is a limited supply of a product and more supply than they can cater for. This is the case with many concerts and sporting events. This means fans may have
to pay higher prices and even then, still may not be able to get a ticket. Where supply is elastic there may be little chance to negotiate over price. You can get as much electricity as you like but you pay the same amount per kWh.
The importance to producers
In general producers will want to have good elasticity of supply so they can respond to changing market conditions. To improve their elasticity firms might:
* Adopt new technology or improve the technology they have.
* Add spare capacity which for a bar might mean having more staff on to cater for a greater number of people or for a factory it might mean running equipment at 80% so if there is need for a rush a job or a problem it can be
dealt with promptly. A shop might add spare capacity by keeping more stock on hand.
* Improve the shelf life of products by changing their packaging.
* Ensure that staff are trained to perform multiple roles so they can more easily be deployed to the areas of greatest need at any given time. If you watch when you go on a flight you will often see some of the same people at check-in,
at the boarding gate and on your flight. Because they are trained on many roles it is easier to cover if people are late or off.
Exam style questions
Use the space below each question or a pen and paper to write your answer. When complete click the button for the answer and mark scheme.
NOTE: Answers typed into the browser will not be retained if you leave the page or refresh
Questions
Explain what is meant by supply. (2 marks)
The willingness and ability(1) to supply goods or service at each price in a certain time period.(1)
Explain what the law of supply is. (2 marks)
The supply of a good or service is directly related to the price(1) i.e. as the price rises so does demand and vice versa.(1)
Explain how the difference between individual demand and market supply. (2 marks)
Individual demand is the amount of a good or service that an individual would buy at each price in a given time period(1)
Market demand is the total demand from all potential customers at each price in a given time period.(1)
Draw an inelastic supply curve. (2 marks)
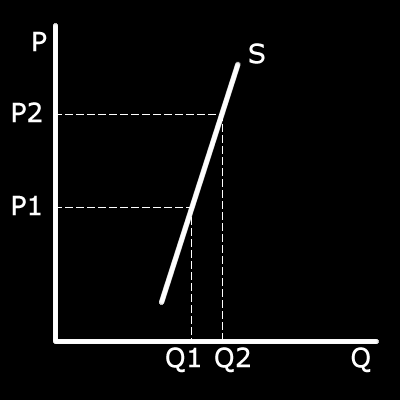
You don't have to draw the dotted lines but you need to make sure you labelled the x and y axis and the supply curve itself.
You should
have drawn something that is very steep and nowhere near 45 degrees.
1 mark for the line at the right angle, 1 mark for all the labels.
Explain what price elasticity of supply is. (2 marks)
The responsiveness of supply(1) to a change in price.(1)
Case study/Scenario
Northwest Offshore is a new British offshore wind farm that aims to be able to produce enough energy to supply the entire North West of the UK within 5 years. Because this will help the government to reach emissions targets
Northwest Offshore receives subsidies from the government. Demand for energy tends to be fairly inelastic.
Analyse the consequences of these subsidies on Northwest Offshore. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
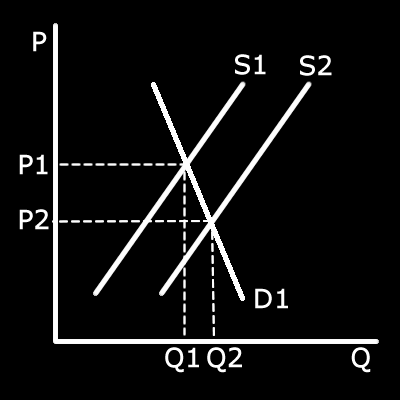 Right shift of supply with inelastic demand
Right shift of supply with inelastic demand A maximum of 4 marks if no correct diagram
The subsidy will lead to an increase in supply{AO1} which is a movement along the demand curve {AO2} These first two points can be obtained from the diagram.
A rise in supply is likely to lead to large reduction in
equilibrium price {AO3a} and a smaller increase in demand for green energy{AO3a}. This could allow Northwest Offshore to make more profit{AO2} that can be re-invested into the business to make it more efficient.{A03a}
Additional notes:
Make sure you are in context. Here I have talked about electricity.
It's an analyse question so you are looking to provide a piece of knowledge. Then you need to apply it twice and analyse what that means.
Here showing the effect on equilibrium price and quantity is one application and discussing the potential effects for the company is the other.
There is no need for
a concluding statement.
Case study/Scenario
Sophia runs a home made Gelato shop on the beachfront in the popular tourist resort of Beachington Heads. She makes all the ice cream herself for the shop. Most have her sales are made in the spring and the summer where Sophia
thinks the most important factor in how well she do is the weather with more people wanting a gelato in good weather. In addition the town host an annual music festival which sees thousands of festival goers visit the local area.
During the festial and on some particularly warm summer days Sophia runs out of some of her best selling flavours of ice cream. Her shop is only small and to be able to put in more refrigerated storage would require her to apply
for and build an additional refrigerated storage unit onto the back of the business.
Evaluate the importance of price elasticity of supply to Sophia. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
Sophia is in a situation where demand will fluctuate. There will be a lot of people when the festival is on and when it is warm and less when it is the cooler months or raining.{AO2}this means it is important
for her to be able to supply more ice cream at times of high demand such as sunny summer days and during the festival.{AO3a} This might mean having more ice cream on hand so that she doesn't run out of people's favourite flavours
leading to lost sales, disappointed customers and poor reviews. This may mean fewer customers in the future.{AO3a}
However, if she is unable to get permission to expand the storage{AO3b} or if the cost of making the changes
to the store cannot be justified for the one off festival when a lack of sunshine may mean there is little need for it in the summer.{AO3b}
In general it would normally be important for Sophia to increase her PES and take
advantage of the warm days and the music festival but if the costs are high compared to the income she can make or if she can't get permission to expand then it is not as important.{AO3b}
Additional notes:
Context is
achieved by talking about ice creams and referencing facts from the scenario like the festival and running out of ice cream.
This is a slightly different type of evaluate. You wouldn't say price elasticity isn't important
for anyone. It's always best to be able to adjust to the demand you get. So in this case to evaluate it we are saying to what extent does it matter.
<< Previous: Demand Next: Price >>