Employment and unemployment
The labour force is the people in a country that could be workers. There are some people that are not a part of the active labour force such as children, students, pensioners and the ill. Unemployment is when people that are
part of the active labour force are both willing and able to work at the current rates but cannot find a job. Employment is when firms pay for the resource labour to produce goods and services.
There are two key ways to measure the size of unemployment: the claimant count and through a labour force survey.
The claimant count measure the number of people receiving unemployment benefits. There may be some reasons why this may miss some members of the active labour force that are not currently employed. People who are not working
but can afford not to seek benefits ad choose not to would not be counted. Nor would those temporarily without jobs.
A labour force survey involves contacting households directly and asking questions about employment. This uses international standards making it easier to compare unemployment figures between countries.
Analyse recent and historical unemployment figures
Trading economics is once again the best place for this data. You will find unemployment under the labour tab after you select a country. Remember the keys from before: where does
it start, where does it end is there a trend and is it steady or are there some fluctuations. To analyse the 10 year unemployment graph for the UK shown below I would say:
At the start of the period in 2012 the UK had a high unemployment rate of 8%. This came steadily down until it reached just below 4% in 2019. There was a short lived increase in unemployment due to the pandemic but otherwise
it has remained steady just below 4% since.
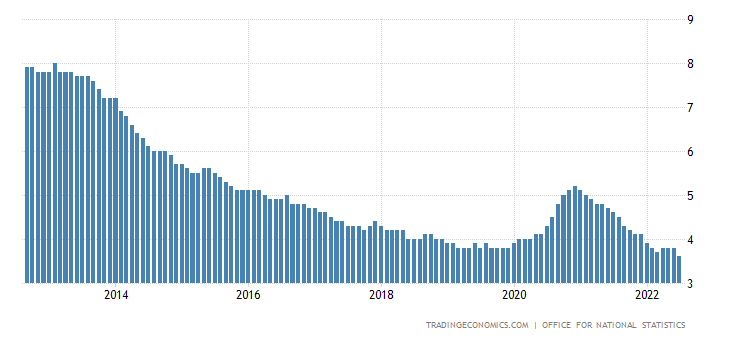 UK unemployment rate courtesy: Trading Economics - ONS
UK unemployment rate courtesy: Trading Economics - ONS
In an analyse question as well as talking through what you see you would need to talk about its flow on effects. For instance, a decrease in the unemployment rate means incomes are rising as having a job pays more than
benefits. Now it depends who you are asked to analyse the effect of it for. For individuals that is good because they can get more of the things they want and have a higher standard of living. For firms this is good because
there is an increase in demand because people have more money and this can lead to higher profits. For the government it is good because they pay less in benefits and get more in taxes meaning they have more money to spend on
areas they feel desrve it.
Types of unemployment
| Type of unemployment |
Description |
| Cyclical |
Economies tend to move in cycles of booms and busts. Cyclical unemployment is when unemployment is the result of a drop in demand. This can lead to a vicious circle because lower demand means less workers are needed
but as some workers lose their jobs incomes fall further. |
| Frictional |
This is a form of unemployment that occurs when someone is moving between jobs. Rather than being a problem frictional unemployment can show that the labour force is adapting to be a part of new growing industries. |
| Seasonal |
This is where workers are only employed in certain seasons such as beach resorts in summer and ski resorts in winter. Fruit picking times are dependent on when crops develop and so tend to be seasonal. |
| Structural |
This is where an industry goes into decline or collapses and the workers that are made unemployed lack the skills and qualifications needed for new opportunities in their area. As the industry declines so to property
values in the area and it may not be a viable option for people in areas of structural unemployment to move. |
The reality is that in many cases several of these factors may have had a role in unemployment in a particular scenario. They do not have to exist in isolation.
Exam style questions
Use the space below each question or a pen and paper to write your answer. When complete click the button for the answer and mark scheme.
NOTE: Answers typed into the browser will not be retained if you leave the page or refresh
Questions
Explain what is meant by unemployment. (2 marks)
When people who are able and willing to work for the current rates(1) cannot find a job.(1)
Explain what the claimant count is. (2 marks)
A measure of unemployment(1) that is based on the number of people claiming unemployment benefits.(1)
Explain what frictional unemployment is. (2 marks)
When workers are temporarily unemployed(1) as they transfer from one job to another.(1)
Explain what structural unemployment is. (2 marks)
When an industry goes into decline(1) and the workers from that industry don't have transferable skills to easily get new jobs.(1)
Explain what seasonal unemployment is. (2 marks)
This is where a job only really exists in one season such as ski resorts in winter or beach resorts in summer(1) Therefore many people in these areas are unemployed in the off season.(1)
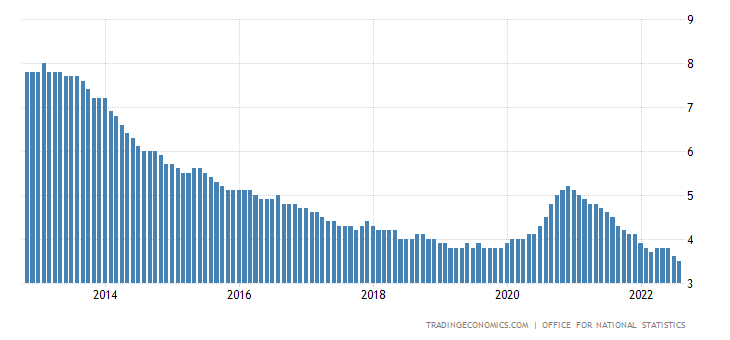 UK Unemployment rate last 10 years
UK Unemployment rate last 10 years
Analyse the effects of recent unemployment trends on the UK. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
The unemployment rate measures the number of members of the active labour force that are out of work.{AO1} The UK has had a steadily declining unemployment rate throughout the period with a small backstep
caused by the pandemic.{AO2} This means higher wages for UK citizens{AO3a} and a higher standard of living.{AO3a}
It also means less money spent by the government on paying benefits{AO2} resulting in more money for them to
spend in other areas such as health improving the welfare of the population.{AO3a}
Case study/Scenario
Evaluate the consequences of unemployment for the government. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
When unemployment increases more people require benefits{AO2} This means the government has to pay more in benefits and recieve less in income tax{AO3a} The level of unemployment will have a big impact on how
important this factor is.{AO3b}
The lower average incomes caused by unemployment can lead to lower spending which can lead to further unemployment and a vicious cycle of decline.{AO3a}. The level of unemployment and the actions the
government takes to stop this cycle will determine how important it is.{AO3b}
Unemployment is of major concern if it gets high as it can cause further unemployment but of less concern if managed at low levels.{AO3b}
<< Previous: Economic growth Next: Fair distribution of incomes >>