Government spending and sources of revenue
Fiscal policy refers to the way the government earns money and spends it.
The government spends money in a large number of areas. By far the largest expenditure is on social protection which refers to the system of benefits, followed by health and education. Some spending like defence which
is the armed services and public order and safety which includes the police and emergency services provides services that may not be viable to be provided as commercial services.
Income tax and national insurance which are collected from employees before they receive their wages along with VAT on sales represent the three biggest areas of income for the government. They also raise money from
other taxes, business rates, excise duties and from other sources.
| Type of tax |
Description |
Example |
| Direct tax |
Direct taxes are taxes on income or wealth |
Income tax, coprorations tax, inheritance tax |
| Indirect tax |
Indirect taxes are taxes on spending |
VAT, excise duties |
Balanced, surplus and deficit budgets
The governments budget sets out their planned spending against their planned income. If these were to be exactly equal it would be known as a balanced budget. It is extremely rare to see a perfectly balanced budget. When
the government plans to spend more than it earns it is known as a budget deficit. When they plan to spend less than they earn it is a budget surplus.
In the UK the last year with a surplus budget was 2000 and looking further back they are quite rare in the UK.
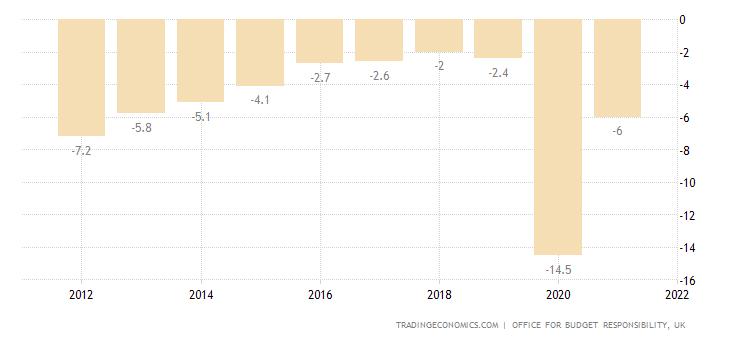 UK government budget as a % of GDP - courtesy: Trading Economics - ONS
UK government budget as a % of GDP - courtesy: Trading Economics - ONS
What is fiscal policy
Fiscal policy is the governments use of tax and spending to meet their 4 major economic objectives. The 4 major objectives are:
* Economic growth
* Low unemployment
* Price stability
* Better balance of payments
Some of these objectives are at odds with each other. The government must decide whether a surplus or deficit budget will better help them to achieve their goals.
Effects of a deficit budget
This could happen either because of lower government income or because of higher government expenditure.
If the government spends more say on health or infrastructure projects, then that money becomes income for the firms that provide the goods and services. This can help to increase demand stimulating job growth and increasing
output and therefore economic growth.
If the government lowers taxes like income tax, then people will have more money to spend on goods and services they want leading to a right shift of demand meaning more workers are needed to produce the additional output.
If they lowered taxes for firms then they would be more willing to supply at each price meaning a right shift of supply and more output.
Effects of a surplus budget
This could happen either because of higher government income or because of lower government expenditure.
If the government reduces its level of spending there is less income for firms. This reduction in demand means firms need fewer workers. This creates a downward spiral of lower incomes leading to lower output needed and further
job losses.
If the government raises taxes like income tax, then people will have less money to spend on goods and services they want leading to a left shift of demand meaning less workers are needed to produce the reduced output. With
lower incomes there is less upward pressure on prices from demand. If they raised taxes for firms then they would be less willing to supply at each price meaning a left shift of supply and less output.
Calculate and analyse how taxes and government spending can affect markets
| Type of tax |
Increase/decrease |
Effect on markets |
| Direct tax |
Increase |
If income tax goes up then people may not feel like it is worth the effort to seek extra work or a promotion if the after tax reward is lower. If corporations tax is higher then firms may be discouraged from investing. |
| Decrease |
If income tax goes down then people may be more willing to seek extra work or a promotion if the after tax reward is higher. If corproations tax is lower then firms may be more inclined to invest. |
| Indirect tax |
Increase |
If VAT goes up then the price of goods and services that have VAT goes up and so demand will go down. Excise duties are used to make selected goods very expensive in the hope of discouraging their consumption. |
| Decrease |
If VAT goes down then the price of goods and services that have VAT goes down and so demand will go up. When VAT is low consumers also have more money to spend. |
Government spending
As you see in the table at the top of this page the government spends a lot of money on health, education, the military, transport and other areas. The money they spend is income for the firms that supply the goods and services they
need. This then goes on to have a multiplier effect with this extra income generating more demand. On the other hand when the government reduces spending there is less income for everyone leading firms to reduce output and leading to
a negative spiral of unemployment and lower demand.
The government can use its money to provide subsidies. This can help encourage growth in areas with positive benefits like renewable energy or encourage investment in deprived areas or provide support to help grow small businesses
or exports.
Evaluate the costs and the benefits of fiscal policy
Regardless of whether the government runs a budget deficit or a budget surplus they may not get the exact result they want and there may be unexpected consequences.
If the government has reduced taxes to encourage growth and employment then their is no guarantee people will spend their increased disposable income or that firms will invest. In addition increased spending may be on imports
negatively impacting the balance of payments. In addition the increased incomes could lead to demand-pull inflation if supply cannot match the increased demand created.
If the government increases spending in one area it must either reduce it in another or increase government debt. There will always be an opportunity cost to their spending decisions.
If the government increases taxes to reduce pressure on prices, it could lead to individuals seeking a pay rise to maintain their living standards. This could lead to cost-push inflation. If they hope that it will improve balance
of payments, it could turn out that people pay the higher price for the imported goods and have less left over for other goods that may not be imported.
Evaluate economic consequences of measures to redistribute income and wealth
| Measure |
How it can redistribute wealth and income |
Possible consequences |
| Progressive taxes |
Progressive taxes mean as incomes increase so to does the percentage of tax that is charged on that income. This is the case with the current income tax system. Those who earn the least pay no tax, then those that
earn more than £12,570 pay 20% on each pound over that up to £50,270. Then the rate is 40% on income between £50,271 and £150,000 and 45% on inome over £150,000. Although a recent announcement
will see the 45% tax rate scrapped soon and the lowest rate swithced to 19%. |
If income tax is high then it may discourage some people from seeking extra hours or promotions because the after tax reward is not enough. Some of the wealthiest people may move abroad and become non-domocile residents
meaning they don't pay tax in the UK. |
| Benefits |
The provision of benefits seeks to ensure that everyone has enough to meet their basic needs by providing incomes to the unemployed, retired and long term ill. This is funded through the taxes of working people. |
If benefits are viewed as generous then some people ay be discouraged from working because the reward for working is not enough more than benefits. |
| National minimum and living wage |
The national minimum and living wages set out the minimum amount that can be paid to employees for their labour. This helps to ensure low skilled workers can earn a decent wage. |
Increases to the minimum and living wage rates might lead to firms employing less staff. |
| Decrease in indirect taxes |
If VAT goes down then the price of goods and services that have VAT goes down. VAT is known as a regressive tax as it represents a higher proportion of income for low earners. Therefore by reducing VAT the benefit
will be felt most by low income earners. The same could be said of exicse duties although the government generally keeps taxes on these high because of the negative externalities they generate. |
A decrease in VAT means the government has less money to redistribute. |
Knowledge check
Exam style questions
Use the space below each question or a pen and paper to write your answer. When complete click the button for the answer and mark scheme.
NOTE: Answers typed into the browser will not be retained if you leave the page or refresh
Questions
Explain what is meant by spending on social protection. (2 marks)
Money spent on system of social security benefits(1) for the unemployed, ill and retired.(1)
Explain what capital gains tax is. (2 marks)
If you sell an asset like a house for more than you paid for it(1), Then you pay capital gains tax on the difference between the sale price and the original price.(1)
Explain what is meat by excise duties. (2 marks)
Special additional fees(1) levied on goods with negative externalities like petrol and alcohol.(1)
Explain the difference between a direct tax and an indirect tax. (2 marks)
A direct tax is a tax on income or wealth(1) whereas an indirect tax is a tax on spending.(1)
Explain the what a surplus budget is. (2 marks)
Where government income from taxes and other sources(1) exceeds government spending.(1)
State the two economic objectives of the Government that might be helped by a budget deficit. (2 marks)
Economic growth(1) Low unemployment(1)
Case study/Scenario
The Labour party have recently suggested that if they are elected they will create a publicly owned energy company called Great British Energy similar to firms like EDF from France and other nationalised energy firms.
The company would be encouraged to invest in clean energy technologies - wind, solar, tidal, nuclear and other emerging technologies. It is thought it could bring in between £60 billion and £120 billion over
the next two years if we had one. Although the long term aim would be for the firm to turn a profit it is likely to take some time to do so and be extremely costly to set up. If investments are in riskier emerging technologies
they may not be guaranteed to succeed.
Evaluate the costs and benefits to the UK of a publicly owned energy company. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
A government owned energy company could produce a significant income stream for the government in the future.{AO2} This means they woud have more money available to spend without having to incur debt{AO3a}
and with increased spending on areas like health and social care people have a better quality of life.{AO3a}
However this could cost a lot of money to set up now which is not completely guaranteed to generate income in
the future. This means their is an opportunity cost to using money for this purpose{AO3b}and some people may feel it is better off spent on other projects.{AO3b}
If the government is able to set up a profitable energy firm
in a short space of time then it will be very beneficial, but if it takes a long time to recoup the money or the business fails then people will feel the money could have been better spent.{A03b}
Case study/Scenario
In the UK we use a system of progressive taxes as shown below:
| Income level |
tax rate |
| Up to £12,570 |
0% |
| £12,571 - £50,270 |
20% |
| £50,271 - £150,000 |
40% |
| Over £150,000 |
45% |
It is sometimes mistakenly thought that you can pay more tax by moving into the next tax band. However, this is not true as you only pay the higher rate on the amount of your income that is over the threshold.
Evaluate the consequences of of using progressive taxes to redistribute income in the UK. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
Progressive taxes mean that more tax is collected from those who earn more income.{AO2} This money can be used by the government to provide benefits and pay for education and health{AO3a} which is good for society
and reduces the gap between the rich and poor by giving the poorest benefits and ensuring everyone has access to basic services.{AO3a}
Some high earners may move abroad to avoid high progressive taxes{AO3b} leading to a loss of
their skills in the country and of their tax revenue.{AO3b}
Progressive taxes help to redistribute incomes more fairly but if they cause high income earners to move away then they will be less effective in achieving their goals.{AO3b}
<< Previous: Price stability Next: Monetary policy >>
© All materials created by and copyright S.Goff