Analyse recent and historical exchange rate data
Using Trading economics you can click Markets and then Currencies and select the currency market you wish to view.
The price of GBP in USD has fallen from $1.60 at the start of the period to a low around $1.10 at the end. It has fluctuatd throughout but was relatively stable between $1.20 and $1.40 from 2016 until recently when it reached
new lows. You might then get asked to explain how that impacts holiday makers from these countries or firms that trade between them.
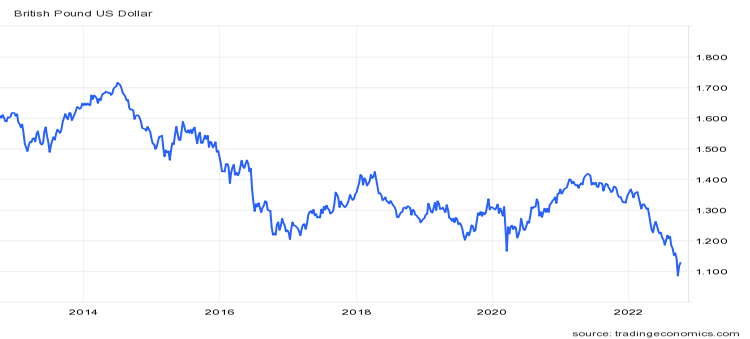 Exchange rate for GBP to USD for the past 10 years
Exchange rate for GBP to USD for the past 10 years
Evaluate the effect of changes in the exchange rate on consumers and producers
| Effect of an appreciating exchange rate |
How it affects consumers |
How it affects producers |
| Imports |
Comsumers get cheaper imported goods and services and may buy more of these. |
Producers who import supplies for their production will benefit from lower costs which may mean they can lower prices and be more competitive. |
| Travel |
It is cheaper for UK residents to travel as they can get more for their pound on holidays. |
For firms that work in the travel industry this provides additional demand. |
| Lower interest |
Comsumers with mortgages or those who wish to get one may benefit from lower rates and be left more disposable income because the Bank of England lowers rates to try to encourage investment to improve the UK's
competitiveness. |
Producers who wish to expand and benefit from economies of scale so they can become more competitive benefit from these lower interest rates too. |
| Lower inflation |
Consumers benefit from the certainty of lower inflation because lower exports and higher imports means less overall demand in the country reducing demand pull inflation. |
Lower inflation means less pressure on wages which in time can help the country back towards being more competitive. |
For a depreciating exchange rate the effects are likely to be the opposite. Imports are more expensive which will reduce their consumption while our exports are cheaper and so we may be able to export more. This might mean
more workers are needed to make the additional output needed for export. This would improve the country's balance of payments. The extra incomes this generates can be inflationary if supply cannot keep up with the demand from
our now wealthier workforce. It will be more expensive to take a foreign holiday but more foreign tourists may be attracted to the UK which will benefit firms in the tourism and hospitality sectors.
The key thing to remember is whether it is appreciating or depreciating there will be both people who benefit and people who are worse off.
Exam style questions
Use the space below each question or a pen and paper to write your answer. When complete click the button for the answer and mark scheme.
NOTE: Answers typed into the browser will not be retained if you leave the page or refresh
Questions
Explain what an exchange rate is. (2 marks)
The price of one currency(1) expressed in terms of another.(1)
Explain what a currency is. (2 marks)
The system of money(1) used in a country or group of countries.(1)
Explain how the exchange rate for GBP in USD is determined. (2 marks)
By the interaction of British consumers who supply GBP in return for USD they need for purchases from the US(1) and US consumers who demand GBP to buy British goods and services.(1)
Jacob is taking a trip to the USA. If £1 buys $1.10 US how much US spending money will he have when he converts his £1000 he has saved to take on the trip? (2 marks)
1000 x 1.10(1) = $1100(1)
Fred is in the USA but wants to purchase some supporter gear for his favourite Premier League team Chelsea. He has a budget of $100 US. How much is the most his items can cost in GBP to the nearest penny before he goes over his budget if
£1 buys $1.10 US? (2 marks)
100 / 1.10(1) = £90.91(1)
Case study/Scenario
Analyse the effect of rising interest rates in the UK compared to other European countries on the market for GBP in EUR. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
If interest rates rise faster in the UK than elsewhere then the UK is a better place to save money.{AO1} More firms and individuals will want to save money in UK banks.{AO2} Leading to a right shift of demand{AO3a}
and causing the equilibrium price of GBP in EUR to rise.{AO3a} The size of the difference in interest between the UK and other countries will affect the degree of change{AO2} with a larger gap resulting in bigger rises.{AO3a}
Case study/Scenario
In 2014 the GBP-USD exchange rate was £1 was worth $1.71 and it has declined now to £1 is worth $1.10.
Evaluate the effects of these chages on UK producers. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
The decrease in value of the pound would mean British exports were cheaper to US consumers{AO2} This could mean that they are able to sell more goods in the US{AO3a} and make more profit.{AO3a}
However,
for producers who use inputs to production that come from the US those inputs will be more expensive, meaning they may have to raise prices{AO3b} which could result in lower sales and profit.{AO3b}
For producers that are exporters the effects could be very positive but for those that import goods from the US they could be very negative.{AO3b}
<< Previous: Balance of payments Next: Globalisation >>