Pay and tax calculations
| Pay and tax term |
Description |
| Gross pay |
This is the total amount of pay an employee receives before any deductions are made. |
| Net pay |
This is the total amount of pay an employee receives after any deductions are made. |
| Deductions |
Income tax, national insurance and pension contributions come out of an employees wages before they receive them. |
| National insurance |
This is an amount paid by workers towards the cost of state benefits. |
| Pension |
A pension is a fund that you pay into regularly while you are working and when you retire you receive the money and interest either as a lump sum or as an annuity which is a series of regular payments. |
| Income tax |
Income tax is the amount of tax you pay for earning money above the tax-free threshold. |
The myth about higher income and higher tax
It is true that in the UK we have a sliding tax scale with more tax payable on higher incomes. The current tax rates can be found on the government's website here
The important thing to note is that you only ever pay the increased level of tax on the income you earn that is above the threshold for that tax level. Because of this going into the tax bracket will never cause someone's
income to drop. It may however mean that the extra amount they earn for doing a little more work may not be of as much benefit if it pushes them into the next tax bracket.
Calculating Gross & Net Pay
Gross pay is made up of a persons basic pay including bonuses and overtime pay.
A person earning £2000 basic pay plus £200 in overtime pay in a month has gross pay of £2000 + £200 or £2200.
Net pay is after deductions are made from gross pay. Let's assume our employee pays £400 tax, £200 national insurance, and pension contributions of £100.
So net pay = gross pay - deductions = £2200 - (£400 + £200 + £100) = £2200 - £700 = £1500.
Click the button below to generate a question to practice calculating gross and net pay
Exam style questions
Use the space below each question or a pen and paper to write your answer. When complete click the button for the answer and mark scheme.
NOTE: Answers typed into the browser will not be retained if you leave the page or refresh
Questions
Explain what is meant by the labour market. (2 marks)
Where households supply there labour(1) to meet the demands of firms for workers.(1)
Explain the role of trade unions in the labour market. (2 marks)
Trade unions are groups that represent employees(1) and advocate for better pay and conditions.(1)
Explain what net pay is. (2 marks)
net pay is the pay a worker receives after deductions(1) like tax and national insurance.(1)
Explain what national insurance is. (2 marks)
National insurance is a contribution collected from the income of workers(1) to contribute toward the provision of state benefits.(1)
Explain what a pension is. (2 marks)
A fund workers pay into each pay check throughout their lives(1) that pays out when they retire either as a lump sum or an annuity.(1)
Case study/Scenario
When Britain went through the process of Brexit it made it more difficult for European workers to work in the UK. This has had a particular impact on the fruit farming industry who have found it hard to get enough pickers and
packers.
Analyse the effect of this on the UK labour market for fruit farm workers. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
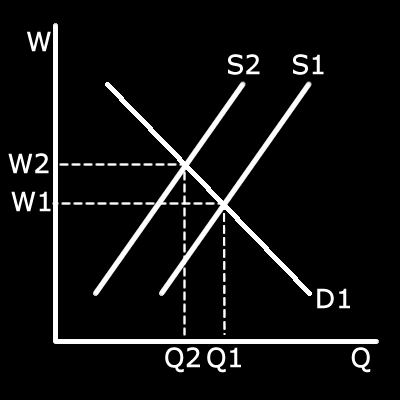 Left shift of supply of workers
Left shift of supply of workersMax 4 marks without correct graph
Because there are less workers British farms who relied on European workers{AO2} have had to pay higher wages{AO3a} and in some cases have still not been able to get enough pickers leading to wastage{AO3a} This leads to lower profits
for Britsh fruit farmers.{AO3a}
Additional notes:
The first two marks are for knowing it means a left shift of supply and drawing it correctly is applying it as you are showing the change in equilibrium.
Case study/Scenario
The UK has a National Minimum Wage(NMW) and a National Living Wage(NLW) for older workers. These specify the minimum amount that firms can pay workers.
Analyse the effect of a rise in the NMW and NLW on the market for minimum wage workers. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
As the minimum wage rises people on minimum wage earn more money{AO1} which may attract more people who are not currently working to work or those working to work more hours{AO2} because they can now earn enough more
than benefits that it is worthwhile to more workers.{AO3a} Meaning a right shift in supply of labour.{AO3a}.
As the minimum wage rises it is a higher cost for firms{AO2} so firms will be likely to demand less labour.{A03a}
<< Previous: Production Next: The role of money & financial markets >>