What is economic growth
Economic growth is the growth in GDP of a country over time. GDP stands for gross domestic product and is the total amount of output for a country in a year. This output is income for the people who produced it in the form
of wages, profits, rent and interest. Therefore when we have economic growth both output and incomes in a country are rising.
Calculate and explain how economic growth is measured
Economic growth can be calculated with the formula:
Growth rate = Change in GDP/Original GDP x 100
Lets say there is a country with GDP of £100b. A year later their GDP has risen to £105b. The growth rate = 5/100 x 100 = 5%
GDP per capita is another measure of economic growth. It is a country's GDP divided by its population. This can tell us quite a bit that the GDP alone may not. If we consider again our country with £100b GDP. If this country
has 100,000 people then the GDP per capita is 1,000,000,000/100,000 = £10,000 meaning that on average people in the country earned £10000. But if this is a country of 1,000,000 people then GDP per capita is 1,000,000,000/1,000,000
= £1,000. This is a big difference. Therefore GDP per capita can be used as a measure of the standard of living between countries. This can still give a distorted view as it does not take into account costs in those countries.
Analyse recent and historical GDP data
Trading economics is an excellent website to use to get access to economic data. This is the countries page. Most if not all countries will have GDP data available. Once
you select a country you will see a GDP tab. Here you will find all GDP related data. Clicking on 'Growth Rate' you will see a page with a chart showing recent GDP growth rates. If you look above the interface allows you to change
the date range you want data to cover, the type of chart and sometimes the ability to compare data.
This skill can be a tricky one for students. In my experience students either say too little or too much. This is likely to be a 2-mark question on an exam. Things to cover in your response. Where did it start and where did it
end. Was there a trend? Was that trend consistent or did it fluctuate? If you have answered these things you should have a good answer. To analyse the UK GDP growth rate seen below I would say that:
Over the past 10 years UK growth started and has remained low but steady with the exception of the pandemic period which saw both large positive and negative growth quarters.
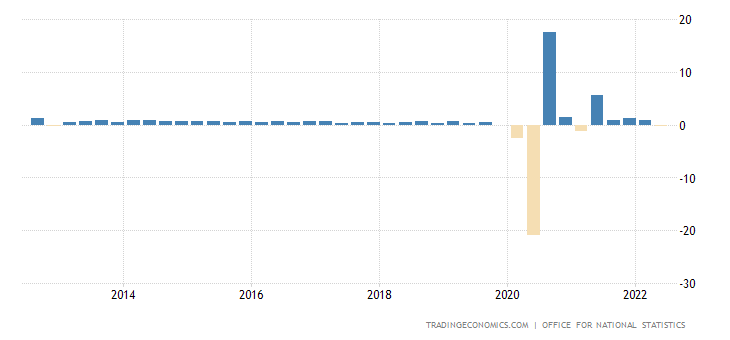 UK Economic growth rate courtesy: Trading Economics - ONS
UK Economic growth rate courtesy: Trading Economics - ONS
You will after explaining the situation have to analyse how that is useful. In this case if you are asked how it might affect individuals you might talk about the low but positive growth meaning on average people would have more
income now than before and so could afford more of the stuff they want increasing their standard of living. For businesses it is positive because people have more money to buy their products leading to higher profits. The government
will benefit from increased income from taxes which they can use to improve conditions for all.
Exam style questions
Use the space below each question or a pen and paper to write your answer. When complete click the button for the answer and mark scheme.
NOTE: Answers typed into the browser will not be retained if you leave the page or refresh
Questions
Explain what is meant by economic growth. (2 marks)
The growth in GDP(1) over time.(1)
Explain what GDP is. (2 marks)
he total output of goods and services(1) produced in a country in a year.(1)
Explain what GDP per capita is. (2 marks)
Gdp i.e. total output of a country for a year(1) divided by the number of people in the country to give an average income.(1)
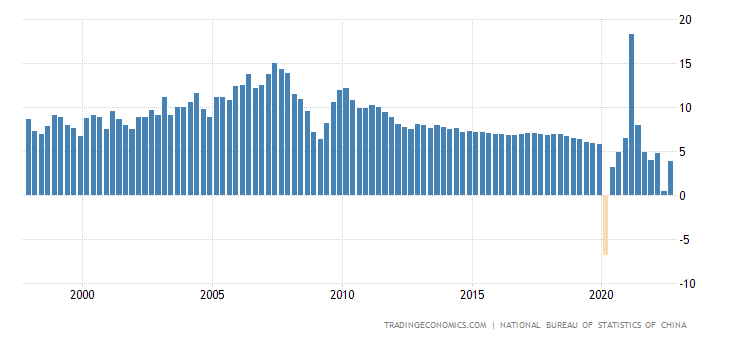 China Economic Growth last 25 years
China Economic Growth last 25 years
Analyse the effect this growth rate is likely to have had on Chinese citizens. (6 marks)
Growth means an increase in output over time which means an increase in incomes becasue output is income for the people who made it.{AO1} China has had consistent medium to high growth for 25 years with the exception of
a few quarters affected by the pandemic.{AO2} This will have mean higher income for individuals{AO3a} and a better standard of living.{AO3a}
It also means more in taxes collected for the government{AO2} which they can
use to improve things for people who need it most.{AO3a}
Analyse the factors that may have led to the sustained economic growth in China. (6 marks)
China is a country where the government plays a very large role.{AO1} The government has consistently invested in major infrastructure projects.{AO2} This provides incomes for the firms and individuals who build this infrastructure.{AO3a}
This then means these people have more money and they then spend that benefiting other businesses in the economy.{AO3a}
China has also opened itself up to greater foreign investment over the same time period.{AO2}
This leads to higher levels of employment which leads to higher incomes and increased demand which when matched by supply means higher output.{AO3a}
<< Previous: Unit 1 Flashcards Next: Low unemployment >>