Why producers compete
Competition is where more than one firm is trying to sell similar products to the same consumers. In a competitive market there are a lot of buyers and a lot of sellers so that no individual can control the market.
The key reason businesses compete is to attract customers and make a profit, but it is not always as simple as that. In reality the reasons and manner in which firms compete changes as businesses evolve.
| Stage of business |
Effects on competition |
| Market entry |
When entering a new market a firm and their products will be unknown. In order to establish themselves they may spend a lot on marketing. They may also offer low introductory prices or even product give-aways in order
to attract customers. If the new player in the market is large, this may force existing firms to respond with their own discounts and offers. |
| Growth |
Once a firm has entered a market they will be looking to survive and then grow. Just to survive and grow a business needs to find a way to both retain existing customers and attract new ones. This may lead to them expanding
their product range to meet the needs of more people. |
| Maturity |
A firm with a developed reputation and solid customer base cannot just sit back and expect that to continue indefinitely. They need to be constantly innovating and developing new and exciting products as well as adapting
current products to better meet the needs of customers. |
The economic impact of competition
The effect on consumers
In general competition provides a lot of benefits to consumers as it can lead to lower prices, innovation and therefore better quality and a wider variety of products. All these things are positive for the consumer giving
them more and or better quality stuff and improving their standard of living.
There can however be negatives for consumers from competition. In an effort to compete producers may use preservatives or chemicals that enhance production or shelf life but have harmful side effects. Some advertising
and methods of promotion may lead consumers to purchase more than they would or things they do not need.
The effect on producers
You might initially think that competition is bad for business as it stands to fore them out of business. While it is true that inefficient firms may be forced out of business by competition, it is generally considered that
competition has positive effects for producers.
Competition forces firms to become more efficient. This leads them to seek out technical innovation. The current computer age has already led to many changes but still stands to revolutionise many processes to the same extent
as the industrial revolution. Automation can greatly increase productivity and if widespread GDP, however it may come at the cost of jobs.
Exam style questions
Use the space below each question or a pen and paper to write your answer. When complete click the button for the answer and mark scheme.
NOTE: Answers typed into the browser will not be retained if you leave the page or refresh
Questions
Explain what is meant by non price competition and give an example. (2 marks)
Non-price competition is where firms compete for customers in ways other than by having the lowest price.(1) e.g. service, quality of product etc.(1) Allow any suitable example.
Explain one way a business at market entry stage may compete. (2 marks)
Needs to be a way and an explanation for two marks:
They might spend a large amount on advertising(1) because they are completely unknown and need to create awareness of their product.(1)
They might offer low prices
or even product giveaways(1) in order to attract new customers.(1)
Explain what an oligopoly is and give an example of one. (2 marks)
An oligopoly is a market where a small number of firms control the majority of the market share.(1) e.g. UK Supermarkets or UK Banks(1) Allow other suitable examples.
Draw a supply and demand graph showing the effect of increased competition. (2 marks)
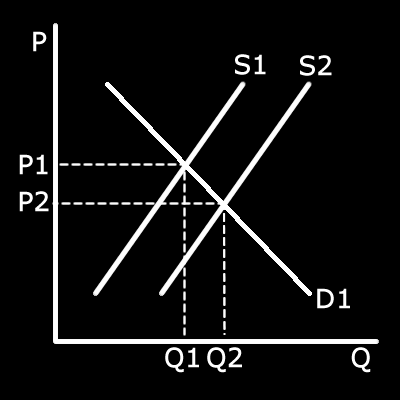 Effect of increased competition
Effect of increased competitionYou don't have to draw the dotted lines but you need to make sure you
labelled the x and y axis and the supply curve itself.
1 mark for showing a right shift of supply, 1 mark for all the labels.
Explain what monopoly power is. (2 marks)
When one firm controls 25% or more of their market(1) they acquire some of the influence normally attributed to a monopoly.(1)
Case study/Scenario
Trevor's Taxis is a taxi firm based in the village of Stonding. You can get other taxis from the nearby town of Swanbridge but only to and from Swanbridge. For trips between Stonding and its neighbouring villages
Gunderidge, Hobden End and Fallstead Trevor's Taxis have a monopoly. These routes are often busy on a Friday and Saturday evening when people often travel between the towns to meet up with friends.
Trevor is thinking about
investing in another two taxis but is concerned about the possibility of another firm setting up in the area.
Analyse the effects on Trevor's Taxis of a new taxi firm operating in the same area. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
Trevor may lose passengers to the new firm{AO1} leading to less demand for his taxis.{AO2} This could lead to lower revenue{AO3a} which may have to make him reconsider his expansion plans.{AO3a}
Trevor may have to decrease his fares in order to attract passengers{AO2} This will mean less revenue if demand is inelastic.{AO3a}
Additional notes:
There are a number of other factors you might have analysed here including
He may have to increase advertising, or have to improve service or compete for drivers with the new firm, all of which would lead to increased costs and so lower profits.
Evaluate the extent to which the locals in the area benefit from Trevor's Taxis being a monopoly. (6 marks)
Sample answer:
Trevor's Taxis will be guaranteed a lot of customers and make a good profit.{AO2} It mentions that Trevor is thinking of investing in more taxis which would mean shorter waits for passengers wanting a taxi{AO3a}
and a better quality of service.{AO3a} However Trevor may realise that his PED is more inelastic because customers have no choices and he may charge higher prices{AO3b}. This means customers would have less money to spend on other
wants.{AO3b}
If Trevor uses his profits to invest in more taxis and people get a better service they may not mind paying a little bit more. However the extent to which he raises prices if he does would have an effect on
whether his customers benefit or not.{A03b}
Additional notes:
Make sure you are in context. Here I have talked about passengers and fares and mentioned his desire to invest in new taxis mentioned in the scenario.
It's an evaluate question so you are looking to cover both sides of the argument.
The concluding statement should say in what crcumstances it will benefit customers and when it won't not whether you think it will or won't.
<< Previous: Price Next: Production >>