Barcode readers
Barcodes can be split into two types: Linear barcodes and QR codes. There are fixed and handheld scanners for barcodes. CCD readers and camera based readers are able to read QR codes.
The pen-style barcode reader must physically touch the barcode. It uses a light source and photo diode that are next to each other. As the pen is dragged across the barcode it detects the level of light reflected back. The
black sections absorb light and the white sections reflect it allowing the scanner to detect the width of the barcode stripes.
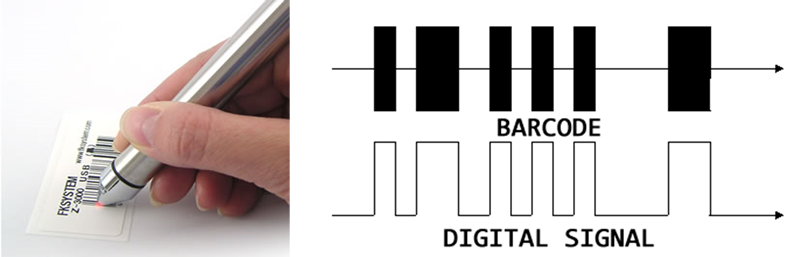
The laser barcode scanners found in most supermarkets use mirrors and lasers to enable barcodes to be read by more angles. CCD handheld devices use an array of sensors that measure the intensity of light that allows them to
reproduce the barcode data as binary information. Because they are handheld and can be wireless, CCD devices can be useful to reach the barcode on unusually shaped or large objects. Camera based readers use a camera and
interpret the image using image processing methods. Some CCD readers can also read 2D style barcodes. This also allows for codes to be read from screens. The images can also be scanned at any rotation and varying distances from
the camera.

Digital camera
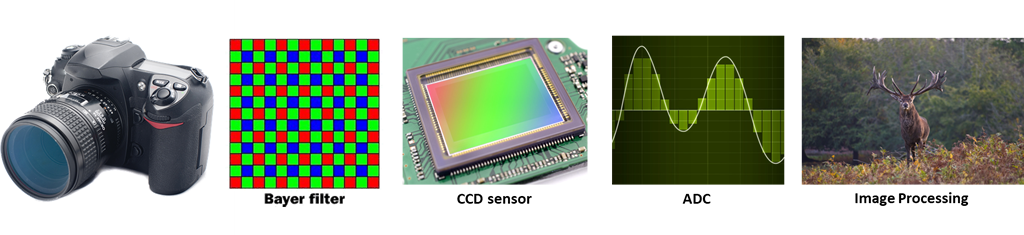
A digital camera has a CCD or CMOS sensor that captures millions of points of light using sensors arranged in a grid. Each sensor measures the amount of light and records it as an electronic value. By doing this with a red,
green and blue Bayer mosaic filter they can get three readings that can be combined to reproduce a colour. The binary readings for red, green and blue for each pixel are recorded to the cameras memory card so the image can be
viewed later with suitable software.
Laser printer
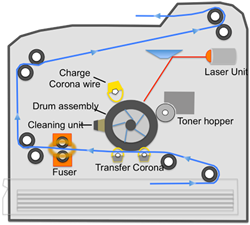
To print a page using a laser printer: The printer creates a bitmap image of the page to be printed. The drum is given a negative charge. A laser light is bounced off a mirror to create a negative, reversed image of the
bitmap which effectively removes the charge from those sections of the page. The page rolls over a roller covered in toner which is positively charged so sticks to the areas that retain a negative charge. The paper passes
through a fuser roller which seals the ink to the page using heat and pressure.
RFID
RFID stands for radio frequency identification. RFID tags can be used in similar ways to barcodes but can be read without needing to be in the line of sight of the reader and from a distance. RFID tags are used for a variety
of purposes such as:
* Pet microchips
* Product tracking
* Automatic toll gates
* Contactless payment
An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. Active RFID tags have a power supply that they use to transmit a signal, allowing them to work at greater distances. Passive RFID tags do
not have a power supply and are instead powered by the radio waves sent out by the reader when they are close enough. This makes passive RFID tags much cheaper to manufacture as well as being able to be very small. The kind used
to microchip pets are only slightly bigger than a grain of rice.
 << Previous: InterruptsNext: Computer Organisation & architecture test >>
<< Previous: InterruptsNext: Computer Organisation & architecture test >>