Processor instruction sets
<< Previous: Processor componentsNext: Assembly language >>
An instruction set is all the operations a processor can perform and their opcodes. Each processor has its own instruction set. Typically an instruction set will include instructions for:
Mathematical calculations, Bit shifts, Comparisons, Logical operators, Branching, Data transfer
Parts of an instruction
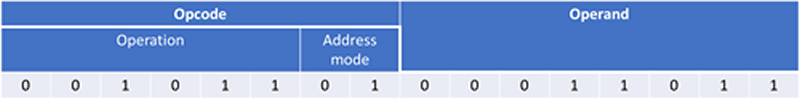
An instruction is made up of three parts:
An opcode that itself is made up of two parts:
An operation that specifies the operation to be carried out
An addressing mode that lets you specify either direct or immediate
addressing
An operand that specifies an actual value or register or memory location depending on the operation
Number of bits used
The number of bits used for the operation, address mode and operand determine how many operations can be requested, how many addressing modes can be used and how many storage locations can be accessed or how big the largest
number that can be entered directly is. The number of operations, address modes and memory locations that can be addressed is 2n where n is the number of bits for the section of the instruction. The largest immediate
number that can be entered is 2n-1