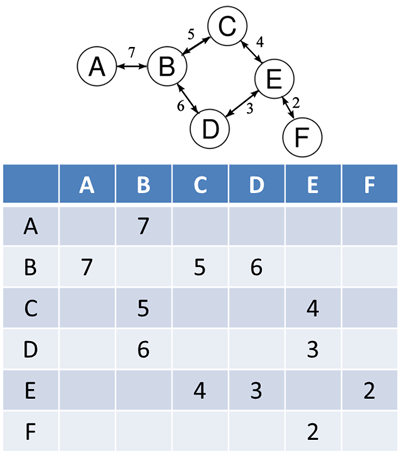
Graphs
A graph is an abstract data type that can be used to represent complex relationships such as the roads connecting towns or the relationships between users on a social networking site. It is made up of nodes, sometimes called
vertices, and edges, sometimes called arcs.
A graph can be either directed or undirected depending on whether it is representing a one or two way connection. In an undirected graph all connections are bi-directional. If all the edges in a graph are one directional it
is a digraph.
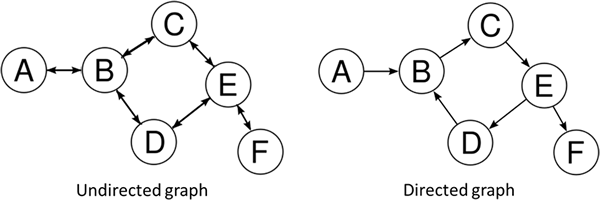
Weighted graphs
A weighted graph can provide additional information about the connections. If we stick with thinking about links between towns it may be that values are for distances, time to travel, or even public transport prices. Other
uses of graphs include social media connections, knowledge graphs such as the hyperlinks between topics in Wikipedia, web pages and their links and more.
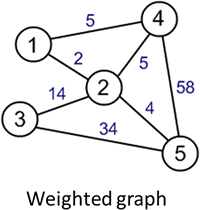
Adjacency matrix
An adjacency matrix is one way to implement a graph. This can be represented with a 2D array. Each column heading is a node. A value at the intersection of two nodes represents an edge between them.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Easy to work with |
A graph with many nodes but few connections takes up a lot of extra space in memory |
| Easy to add and remove edges |
It's hard to add and remove nodes |