Hash tables
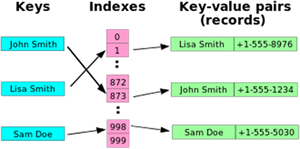
Hash tables provide a way to store a collection of items so that they are easily and quickly accessible. To achieve this a hash table stores an index of the physical address where the data is stored as a key that maps
directly to the value stored in that location. This index is created using a hash function.
Methods for hashing
Hashing is frequently done in two steps:
- Generate a hash
- Use the hash to calculate an index in the hash table
Generating a hash with the folding method
One method that can be used to generate a hash is the folding method. This would break a number up into a series of groups of digits and then add these to provide a hash.
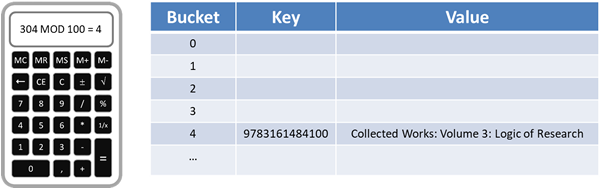
Lets consider an ISBN which is made up of 12
digits followed by a check digit which we will ignore, split into groups of 2 digits. This gives us 97 + 83 + 16 + 14 + 84 + 10 which is a hash value of 304.

Generating a hash from strings
A simple method that can be used to hash strings is to add the ASCII value of each of the characters in a string. "String" = 83 + 116 + 114 + 105 +110 +103 = 631

Calculating an index
One way to calculate an index is to divide the hash value by the number of available spaces in the hash table and return the remainder i.e. use modulus. If we were trying to insert our ISBN from earlier into a hash table
with 100 spaces then it would be 304 MOD 100 which is 4.
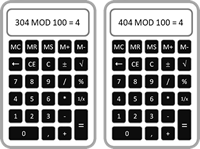
Collisions
If two items result in the same index then we have a collision. An item that shares an index with another is a synonym. If we had another ISBN that resulted in a hash value of 404 this would be a synonym of our earlier ISBN
as it would also return an index of 4.
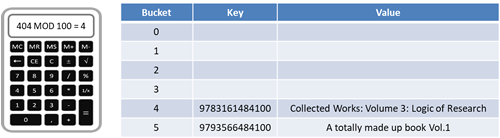
Collision resolution
Any hashing algorithm could result in collisions and so there must be a way to resolve these. Calculating a new location when there is a collision is called rehashing. A basic way to handle rehashing is to place the item in
the next available free space if the space is already occupied. Alternately a set increment or even a variable increment might be used.
Hash tables and Python dictionaries
Python dictionaries are implemented as hash tables. This is an example of functional abstraction as you don't have to know or understand hash tables to use them, just the methods available to python dictionaries.
