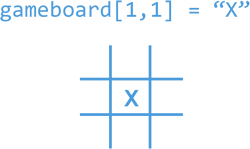Declaring arrays
Arrays are declared by stating the array keyword, the identifier for the array and either:
- Specifying the number of empty slots
needed e.g. array names[5]
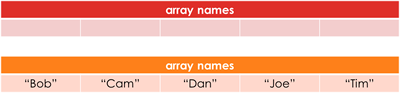
- Specifying the actual values to be assigned to each slot e.g. array names["Bob","Cam","Dan","Joe","Tim"]
Accessing items in an array
Arrays use zero indexing meaning the first item in an array is in position 0. This means the last item is always in position n - 1, where n is the number of items in the array.
Attempting to access an item from a position not in the array results in an out-of-range error.

Assigning values in an array
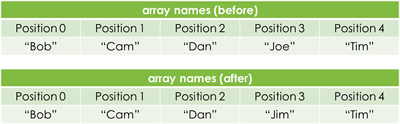
To assign a value to a position in an array you reference both the name of the array and the position you want to assign a new value to e.g. names[3] = "Jim".
2 dimensional arrays
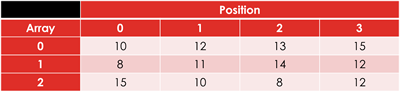
A 2-dimensional array is an array where each element in the array is itself an array e.g. scores = [[10,12,13,15],[8,11,14,12],[15,10,8,12]].
A 2D array is declared by passing two parameters, first the number of sub-arrays and second the number of elements in each sub-array e.g. array gameboard[3,3]
Accessing items in a 2D array
To access data in a 2D array you pass the array name and two values. The first is which sub-array to look in and the second is which position within that sub-array. If we have
an array scores = [[10,12,13,15],[8,11,14,12],[15,10,8,12]] then scores[2,1] would be 10.
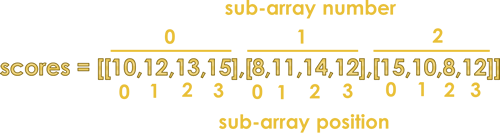
2 dimensional arrays
We pass 2 parameters when assigning to a 2D array, the first is which sub-array and the second which position in that array. gameboard[1,1] = "X" would place an X in the center
of the middle array.