LAN vs WAN
One way of classifying networks is as:
- Local area networks(LANs)
- Wide area networks(WANs)
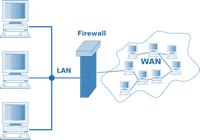
LANs
A LAN covers a small geographic area e.g. a home, office or school. Hardware such as network switches and cables will generally be owned by the people running the network. An office or school may employ technicians to manage
this network.
WANs
A WAN covers a large geographic area e.g. connecting stores across a country or people across the world. Hardware such as network switches and cables will generally be owned by 3rd parties. In the UK the digital network is
managed by Openreach. The primary example of a WAN is the Internet, but firms can also use leased lines to create private secure connections between distant offices.
Factors affecting network performance
There are a range of different factors that can affect the performance of a network, e.g.
- Bandwidth
- Number of connected devices
Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the total amount of data that can be transferred at one time. It is often mistakenly confused with transfer speed. An analogy is often made to bandwidth being similar to the width of a pipe, the wider it
is the more data can flow at one time but it does not affect the speed at which it flows. More bandidth on a network means more devices can communicate at the same time.
Number of connected devices
The number of connected devices has a large effect on wireless networks where all devices share the same maximum bandwidth i.e. total amount of traffic a wireless access point can handle.
Client server vs peer to peer networks
Another way that networks can be classified is by how devices are connected. Two methods you need to be aware of are:
- Client server networks
- Peer to peer networks
Client server networks
In a client server network, powerful machines known as servers provide resources to the less powerful client machines that connect to them. Client server networks often utilize a number of servers for different purposes.

Clients make requests of the servers e.g.
- A student in a school wants to access a web page, so their request is sent to the web server
- A teacher wants to check their emails,
so this request is handled by the email server

Peer to peer networks
Peer to peer networks have no central controlling computers. All computers are connected to each other. Software is used to locate files to download and can download parts of a file from multiple different users who all have
it at the same time reducing download times. Because there is no controlling computer, and files can be stored anywhere peer to peer networks have often been used for illegal file sharing.