Exam style questions
Download a pdf version of the test
Use the space below each question or a pen and paper to write your answer. When complete click the button for the answer and mark scheme.
NOTE: Answers typed into the browser will not be retained if you leave the page or refresh
Questions
Complete the missing parts of the table below (5 marks)
| Data type |
Description |
Example |
| Integer |
A number with no decimal part |
42 |
| Real |
A number with a decimal part |
3.14 |
| Boolean |
For variables that store either true or false |
False |
| Character |
A single letter number or symbol |
'F' |
| String |
A group of characters |
'Bob' |
1 mark per correct answer
 Pseudocode example 1
Pseudocode example 1
On what line does assignment first occur? (1 mark)
On what line does selection first occur? (1 mark)
On what line does iteration first occur? (1 mark)
On what line does assignment first occur? Line 1. Assignment is giving a variable a new value as shown by a left facing arrow in pseudocode.
On what line does selection first occur? Line 5. Selection is completed by an IF
statement or CASE SELECT statement.
On what line does iteration first occur? Line 3. Iteration is looping and this algorithm has a for loop.
What is the purpose of the pseudocode example 1 algorithm above? (3 marks)
It converts each letter in a word(1) to the letter 3 further on in the alphabet(1) and if it goes past Z loops back to A.(1)
Leyla is a photographer who shoots weddings. She charges £125 per hour for her services plus a travel fee of £10 for every 25 miles or part thereof she has to travel. That means for a booking 55 miles away it would
be £30 as it is more than 2 full lots of 25 miles. Write an algorithm that will allow Leyla to enter the number of hours of a booking and the distance to the booking and have it calculate a total price. (5 marks)
hours = int(input("Enter the number of hours worked:"))
miles = int(input("Enter the number of miles travelled"))
cost = hours * 125 + ((miles//25)+1) * 10
print('Total cost: ' + cost)
If not fully correct individual
marks for getting and storing two inputs, muliplying hours by 125, calculating the number of lots of mileage to charge, multiplying that number by 10, calculating and outputting the total amount
Explain what Boolean operators are giving an example of one and explaining how it works (3 marks)
Boolean operators are used to make more complex conditions.(1)
Any pair of operator and explanation from: AND (1) Means both conditions joined together must be true to evaluate as true
; OR (1) Means if either of the joined conditions evaluates as true then the whole thing evaluates as true; NOT (1) reverses the outcome of the condition it is attached to (1)
Write an algorithm that will keep asking the user to answer the question 'What is the capital of England?' until they answer 'London'. When they do it should output how many attempts it took to get it right. (6 marks)
guess = input('What is the capital of London?')
guesses = 1
while guess != 'London'
guess = input('What is the capital of London?')
guesses = guesses + 1
endwhile
print('Attempts:' + str(guesses))
Individual marks for getting user input and storing it; initiating a variable to track attempts; using a while loop; reasking the question in the while loop and getting new input; incrementing attempts variable in the loop;
outputting the number of attempts at the end.
 Pseudocode example 2
Pseudocode example 2
Which of the basic programming constructs can be seen in the algorithm above? (1 mark)
How many subroutines are called in the algorithm? (1 mark)
Explain how you can tell which subroutines are procedures and which are functions in this algorithm? (3 marks)
This subroutine has sequence and iteration.(1) Although there is a comparison it is part of the loop condition not selection.
There are 3.(1) Random_int, Convert_to_letter and displayResult
A function returns a value but a procedure does not(1) so the result of a function must be stored in a variable but a procedure will be called on their own separate line.(1) Convert_to_letter is a function and displayResult is a procedure.(1)
Explain, using examples from pseudocode example 2 above, what a parameter is. (3 marks)
A parameter is a value passed to a subroutine from the main program(1) that can be used within the running of the subroutine.(1) Any suitable example e.g. randNum, userChoice, compChoice(1)
Write an algorithm for a subroutine to get a username from a user and check its length is between 3 and 12 characters. If it is not then the algorithm should give a message saying so and make the user keep re-enter until they enter a username of a valid length. That should then be returned by the subroutine. (7 marks)
function getUsername()
username = input("Enter a username:")
while username.length < 3 OR username.length > 12
print('Must be between 3 and 12 characters!')
username = input("Enter a username:")
endwhile
return username
endfunction
If not completely correct individual marks for: declaring a subroutine; Getting user input; Using a while loop; Correct condition; Message to explain what went wrong to user; new input obtained in the loop; username returned
Explain the difference between local and global variables (3 marks)
Global variables are declared in the main program and local variables are declared inside a subroutine.(1)
Global variables are available throughout the program but local variables are only available in the subroutine where they were declared.(1)
Local variables cease to exist when the subroutine they were part of ends.(1)
Name and describe the three programming constructs (6 marks)
Sequence (1) where code executses one line after the next (1)
Selection (1) where the next code to be run, if any, is determined by the reult of a Boolean condition (1)
Iteration (1) where code is executed more than once (1)
Write a switch statement based on an input num that outputs 'heads' if num is 1, 'tails' if num is 2 and 'invalid input' in all other cases ()
switch num: (1 - correct keyword variable and formatting)
case 1:
print("Heads")
case 2:
print("Tails") (1 mark cases correctly defined)
default:
print("Invalid input") (1 mark default case correctly defined)
endswitch
Write a program that reads and prints all the items in a textfile called shopping.txt (5 marks)
file = open("shopping.txt")
while NOT endOfFile( )
print(file.readLine( ))
endwhile
file.close( )
Marks for opening file with handle and correct name (1) while open and close (1) condition NOT endOfFile (1) readLine() used and value printed inside loop (1) file closed (1)
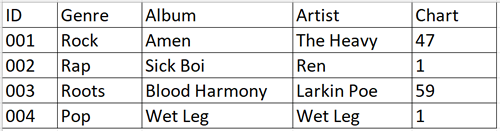
Above is a sample of records in a table called tblAlbums in a database. Write an SQL command to display the ID, Album name and Artist for albums that are in the rock genre and have made the top 10 in the charts (4 marks)
SELECT ID, Album, Artist (1)
FROM tblAlbums (1)
WHERE Genre = 'Rock' AND Chart <= 10 (2 - 1 mark if at least one condition correct and WHERE used)
Write code that will loop through a one dimensional array called scores, that could be of any length greater than 2, and calculate the average of the scores in the array. (5 marks)
total = 0
count = 0
for i = 1 to scores.length
total = total + scores[i]
count = count + 1
next i
print("Average =" + str(total/count))
Marks for: establishing variables before loop (1); any loop that covers all elements (1); new score added to total inside loop (1); count incremented inside loop (1) average
calculated and output (1)
<< Previous: Sub-programs Next: Defensive design >>