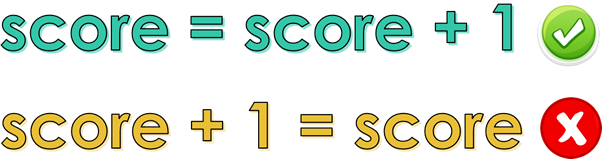Assignment is described at the end of the video after the data types section
Variables vs constants
Variables and constants are both named storage locations for data that might be used in a program. A storage location stores data that will not change throughout the running of the program it is known as a constant. Names of constants are generally in capital letters to identify them as constants. Variables are storage locations for data that may change during the running of the program.
Naming conventions
As well as using capital letters for constants, a number of other rules must be followed when naming storage locations. These include:
- Use meaningful names
- Must begin with a letter or underscore
- Should use camel case or snake case
Meaningful names means they should give you some idea what data will be stored in the location. Camel case is a method that can be used when a variable needs more than one word to be meaningful. With camel case first words start with lowercase and each new word starts with a capital e.g. camelCase. Snake case uses all lower case and separates words with underscores e.g. snake_case. It doesn't matter which you use, but picking one and sticking to it can make it easier to recall your variable names as you type new code.
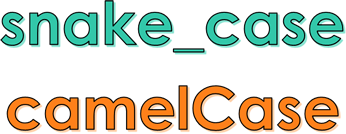
Assignment
Assignment is the act of storing a new value in a variable. Assignment statements must always read from left to right e.g. to assign 7 to a variable called age we can say age = 7 but not 7 = age.