Structure of the Internet
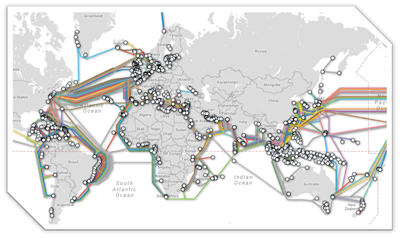
The internet is a network of interconnected networks. The internet backbone is the collection of sub oceanic cables that connect continents. If data is transferred from one location to another within the same land mass it
will likely go from router to router across land. If it needs to go to another continent then it will first head for a major exchange such as Telehouse North in London that can send the data via the undersea cable network.
Data Packets
Data travels on the internet as packets. A data packet is made up of the data itself, often referred to as the payload; A header that includes the sender's and receiver's IP addresses; the number of the packet; and total
number of packets in the transmission; and the protocol being used.

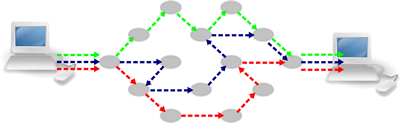
Packet Switching
Packets are sent across the internet from one router to another along the fastest possible path. Each router has routing tables that keep track of the time to other routers it is connected to and these are regularly updated.
Because of changing levels of congestion on different routes packets may travel in different directions to reach their destination.
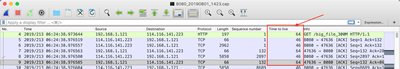
Time To Live
A data packet is given a time to live when it is created. This is a number of hops with each hop being a trip from one router to another. After the hop limit is reached the packet is discarded. If a packet doesn’t arrive at
the receiving end it gets re-requested and terminating them after a set number of hops prevents lost packets unnecessarily cluttering up transmission routes.
Routers and gateways
The role of routers on the internet is to check the destination IP address and send packets along the fastest route to their destination. When data has to be transferred between networks using different protocols then a
gateway is required. A gateway removes the header and adds a new header in the correct format for the new protocol but is otherwise similar to a router in that it passes packets on towards their destination.
Parts of a URL
A URL or Uniform Resource Locater is the full address for a web based resource. The method is the protocol used to access it e.g. https, ftp etc. A domain name is the name someone types into a web browser to find a website
and a fully qualified domain name also includes the host, normally www. Each website has its own IP address e.g. 170.187.185.171

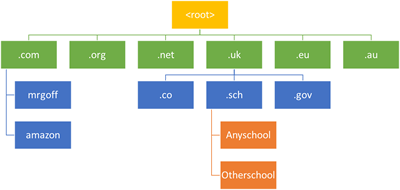
Types of Domain
Domains are organised in a hierarchy. There are two main types of top level domains. Organisation based domains like .org, .com, .net and geographic domains like .uk, .fr, .au. Organisation top level domains may have a second
level domain that relates to the specific organisation eg images.google.com where the 2nd level domain .google extends the top level domain .com. For geographic top level domains the subdomain may specify the type of organisation
e.g. .sch, .co, .gov and these may have a 3rd level domain specifying the particuar organisation. A full web address is read from the bottom to the top of the hierarchy e.g. Anyschool.sch.uk
The domain name system (DNS)
The DNS system is used to translate domain names into IP addresses so their pages can be requested from the web server. A user types in a website domain they wish to visit in a web browser. A request is sent to retrieve the
IP address related with that website. It will first check the local DNS server records on that machine which will store details of recently accessed and frequently accessed sites. If it is not found here it is passed up to a
local DNS normally run by ISPs. If the local DNS cannot return the IP address the request is passed on to a regional DNS. Eventually the request will reach a top level DNS with a record of all domains and IP addresses. Once
found, the IP is returned and used to request a copy of the web page.

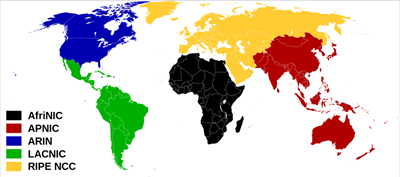
ICANN
Domain names are registered via The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers ICANN and assigned IP addresses. They oversee the 5 internet registries that each hold a database of all the domain names and who owns
them to ensure domain names remain unique.