Firewalls
Firewalls provide a barrier between two networks. Most commonly, the Internet and a private network. They can be hardware or software based. They inspect packets that try to move from one network to another and determine if
they are to be accepted or rejected.

Stateful Inspection
Stateful inspection goes beyond IP addresses, protocols and port numbers and looks at the actual contents of a packet. This can include creating dynamic rules e.g. a person requests a web page and a rule is created to expect
some HTML content from that IP address. This way ports can only be open when necessary to prevent port scanning.
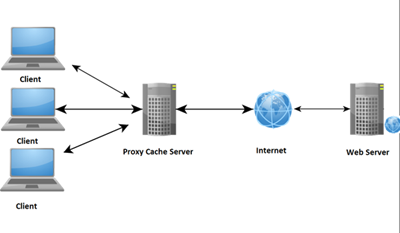
Proxy Server
A proxy server is a server that makes requests on behalf of a client.This way the service which is requested does not know where the actual request came from. A proxy server can also maintain a cache of frequently visited
websites that can be accessed without needing to go online. It can also be used to filter out undesirable requests such as in schools.
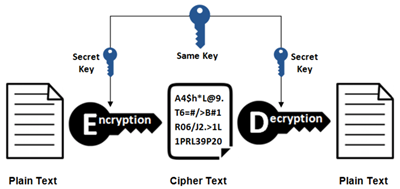
Symmetric key encryption
Symmetric key encryption is also known as private key encryption. This is where data is encrypted and decrypted with the same key. The key and the cipher text must be sent to the recipient leading to security issues. Anyone
who intercepts both can read the message.
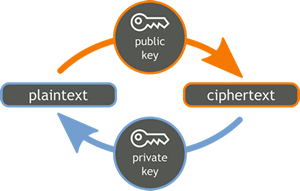
Asymmetric key encryption
Asymmetric key encryption uses two separate but related keys. A public key which can be accessed by anyone wanting to send data to someone and a private key known only by the recipient that can be used to open the message
that has been encrypted with the recipient's public key. Anyone who intercepts the message in between cannot decrypt it without the recipients private key.
Digital signatures
A malicious individual may send you data, encrypted with your public key, that appears to come from another safe sender. Digital signatures can prevent this.
To create a digital signature a sender calculates a hash total from
the contents of the unencrypted message and encrypts it with their private key. This encrypted value and the message are then encrypted with the recipient's public key.
The recipient decrypts the package of the message and the
signature using their private key. They decrypt the signature using the senders public key. They calculate the hash value of the decrypted message and if it matches the decrypted signature then the message comes from the true
recipient and has not changed during transmission.
Digital certificates
Fake digital signatures can be made using a false private key and claiming it belongs to a trusted sender. Digital certificates verify that a public key is formally registered to the sender. They are issued by certificate
authorities. Digital certificates contain: A serial number; Expiry date; Name of the holder; Copy of their public key; The digital signature of the certifying authority.
Viruses
Viruses self-replicate, meaning they create copies of themselves on infected machines. There are many types of viruses and most infect main memory and therefore other files that are loaded into main memory. Viruses are often
attached to other host programs and infect a computer when those host programs are run by the user.
Worms
A worm is a special sub-class of virus. The primary difference is that a worm may infect your machine without the need for user interaction via a vulnerability e.g. unpatched software. A worm may also infect a user who clicks
on an infected link. Worms not only self replicate on your machine but can often spread to other people in your email contacts list.

Trojans
A user infected with a Trojan provides a malicious 3rd party with a back door into their computer. This type of infection is likely to be hidden in another seemingly useful program. There may be few signs that the trojan has
been enacted after the program it is hidden in runs. The 3rd party might use their access to harvest your personal data or to take over your computer and use it as part of a botnet.
