The Internet and the world wide web
Although synonymous in the eyes of many the Internet and the world wide web are not the same thing. The Internet is the set of interconnected networks linked by the globe spanning network of suboceanic cables. The world
wide web is the collection of web pages and other resources hosted on the Internet.
Domain names
A domain name is the unique name by which a website is known e.g. mrgoff.com. Domain names are made up of different levels of domain.
Top level domains include generic domains like .com, .edu and .org, as well as country extensions like .uk .au, and .de
Second level domains indicate the purpose of the website e.g. .gov for government sites and .sch for schools
Third level domains are the name of the website itself e.g. bbc, google, mrgoff
The full domain is all parts joined together.

Domain names service(DNS)
Resources on the internet are actually located using IP addresses. We use domain names because these are far easier for humans to remember. The domain name service, or DNS for short, is used to translate domains into IP
addresses for the web server where the pages are stored.
DNS uses a series of DNS servers in a hierarchy to perform the task. At each level the DNS server will contain more URLs and their related IP addresses until finally a request may reach one of 13 top level DNS root servers
that have all URLs and their associated IP addresses.

Web hosting
Hosting refers to storing web pages on a web server. It is possible to host your own website on a computer you own but most people opt to pay for hosting of their websites with a dedicated provider.
Web servers and clients
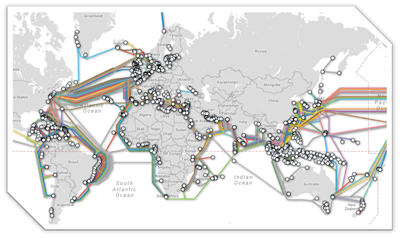
Clients i.e. computers wanting to access websites, use web browsers to access the internet. Client machines make HTTP requests of the web server which can locate and return, or serve, web pages and web applications.
The cloud
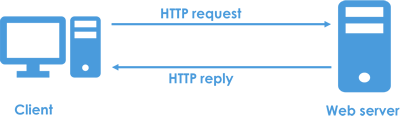
The cloud refers to a series of internet accessed services including cloud storage, cloud applications and even cloud infrastructure.
Cloud storage
Cloud storage is the storing and accessing of files via the internet e.g. OneDrive, Google drive etc.

Cloud applications
Cloud applications refers to software that runs via the internet e.g. Office365.

Cloud infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure refers to the use of virtual services for things like virtual servers, virtual workstations, back-ups and more.